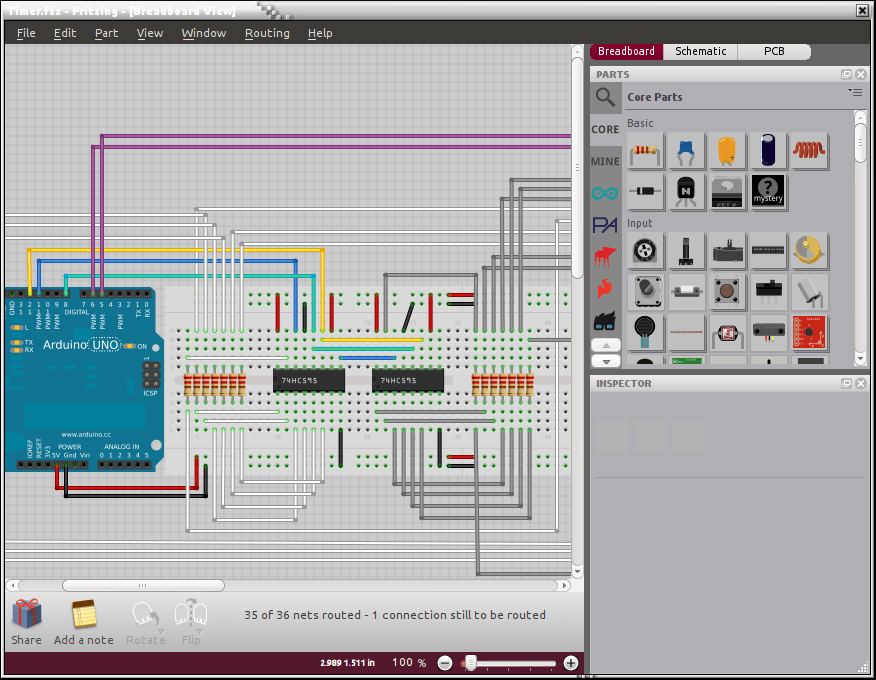
Fritzing is an open source software tool to support designers, artists and hobbyists to work creatively with interactive electronics.
It is designed to help one transition from a prototype to a finished project. Aimed at users who want to produce or document circuits and experiments, one starts by building a physical prototype, then recreating it with Fritzing’s graphical editor. From there one can generate a schematic, PCB artwork, and PCB production files.
Fritzing is essentially Electronic Design Automation software suited to the needs of designers and artists. It uses the metaphor of the breadboard, so that it is easy to transfer a hardware sketch to the software by using a drag-and-drop-based GUI to copy your sketch. From there it is possible to create PCB layouts for turning your prototype into a robust PCB, either on your own, or with the help of a manufacturer.
It was developed at the University of Applied Sciences of Potsdam.
Features include:
- User-friendly interface for a quick and easy workflow:
- Project View – where a virtual electronic circuit is built and edited in breadboard, schematic or pcb view.
-
- Palette Windows – consisting of the Part Library, Part Inspector, Undo History and Navigator.
-
- Part Creator – a tool to modify parts or create new parts for Fritzing.
- Bottom Bar provides quick access to a few of Fritzing’s commands and options.
- Represents electronic parts realistically and takes an intuitive approach to make complex technology usable by non-technologists.
- Breadboard View – looks like a real-life breadboard prototype.
- Schematic View – a more abstract way to look at components and connections than the Breadboard view. This representation is similar to the traditional diagrams used by engineers.
- PCB View – design how the components will appear on a physical Printed Circuit Board. PCBs can be made at home or in a small lab using DIY etching processes.
- Parts Library.
- Several bins. The main bins are “Core” and “Mine”. The Core bin contains all standard parts, where families of similar parts are aggregated into one (e.g., the red LED stands for all the other colors). The Mine bin will contain your custom created parts.
- Autoroute – automatically generate the connection traces between parts.
- Hand-routing.
- Design Rules Check – checks there are no connectors or traces that overlap or are too close together.
- Configurable Design Rules Keepout.
- Ground Fill.
- Zoom in/out.
- Variety of export options:
- Image: PNG, JPG, SVG, PDF, PostScript.
- Production: Etchable (PDF), Etchable (SVG), Extended Gerber. Etchable PDF option exports only the necessary design for etching.
- List of Parts (HTML) – generates a list of all parts in the circuit.
- XML Netlist.
- Internationalization support.
Website: fritzing.org
Support: FAQ, GitHub Code Repository
Developer: Interaction Design Lab at the University of Applied Sciences Potsdam, Germany
License: GNU General Public License v3.0
Fritzing is written in C++. Learn C++ with our recommended free books and free tutorials.
Return to Electronic Design Automation
| Popular series | |
|---|---|
| The largest compilation of the best free and open source software in the universe. Each article is supplied with a legendary ratings chart helping you to make informed decisions. | |
| Hundreds of in-depth reviews offering our unbiased and expert opinion on software. We offer helpful and impartial information. | |
| The Big List of Active Linux Distros is a large compilation of actively developed Linux distributions. | |
| Replace proprietary software with open source alternatives: Google, Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, IBM, Autodesk, Oracle, Atlassian, Corel, Cisco, Intuit, and SAS. | |
| Awesome Free Linux Games Tools showcases a series of tools that making gaming on Linux a more pleasurable experience. This is a new series. | |
| Machine Learning explores practical applications of machine learning and deep learning from a Linux perspective. We've written reviews of more than 40 self-hosted apps. All are free and open source. | |
| New to Linux? Read our Linux for Starters series. We start right at the basics and teach you everything you need to know to get started with Linux. | |
| Alternatives to popular CLI tools showcases essential tools that are modern replacements for core Linux utilities. | |
| Essential Linux system tools focuses on small, indispensable utilities, useful for system administrators as well as regular users. | |
| Linux utilities to maximise your productivity. Small, indispensable tools, useful for anyone running a Linux machine. | |
| Surveys popular streaming services from a Linux perspective: Amazon Music Unlimited, Myuzi, Spotify, Deezer, Tidal. | |
| Saving Money with Linux looks at how you can reduce your energy bills running Linux. | |
| Home computers became commonplace in the 1980s. Emulate home computers including the Commodore 64, Amiga, Atari ST, ZX81, Amstrad CPC, and ZX Spectrum. | |
| Now and Then examines how promising open source software fared over the years. It can be a bumpy ride. | |
| Linux at Home looks at a range of home activities where Linux can play its part, making the most of our time at home, keeping active and engaged. | |
| Linux Candy reveals the lighter side of Linux. Have some fun and escape from the daily drudgery. | |
| Getting Started with Docker helps you master Docker, a set of platform as a service products that delivers software in packages called containers. | |
| Best Free Android Apps. We showcase free Android apps that are definitely worth downloading. There's a strict eligibility criteria for inclusion in this series. | |
| These best free books accelerate your learning of every programming language. Learn a new language today! | |
| These free tutorials offer the perfect tonic to our free programming books series. | |
| Linux Around The World showcases usergroups that are relevant to Linux enthusiasts. Great ways to meet up with fellow enthusiasts. | |
| Stars and Stripes is an occasional series looking at the impact of Linux in the USA. | |