Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is considered to be the fundamental protocol of the web. This simple request/response protocol is used for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. The web consumes a large portion of internet traffic.
With HTTP, a client makes a request for a resource to a server, and the server delivers messages with additional content such as images, style sheets and JavaScript. HTTP dictates how these messages are displayed and transmitted, and how web servers and browsers should respond to various commands.
The developers of the HTTP protocol realized at an early stage that there was going to be rapid growth in web traffic. This continues to be the case.
It is a demonstrable fact that the internet has changed individuals’ expectations of the speed of content delivery. The same individuals who used to be content to wait a couple of days for a letter to be received now expect emails to be delivered within a matter of seconds. The same applies to web browsing. A slow-loading website is a recipe for online disaster even if the site is informative, well structured and organized. When it comes to interactive web usage, what really matters is median latency.
Web caches have become a vital mechanism for optimizing the amount of data that is delivered in a given period of time. Good web caches also help to minimise latency, serving pages as quickly as possible. This helps to prevent the end user from becoming impatient having to wait for content to be delivered. Web caches optimize the data flow between client and server. They also help to conserve bandwidth by caching frequently-delivered content. If you need to reduce server load and improve delivery speed of your content, it’s definitely worth exploring the benefits offered by web cache software.
This type of software is primarily used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs), backbone providers, large intranets and enterprises. Web caches are very versatile, and are used in a number of different systems such as search engines, web proxies, and forward caches.
In this article, we feature the best software that caches web content, optimizing and cleaning the network traffic. The ratings chart below gives our verdict. Only free and open source software is eligible for inclusion. Hopefully, there will be something of interest here for anyone who needs to reduce bandwidth usage, improve latency, and minimise server load.
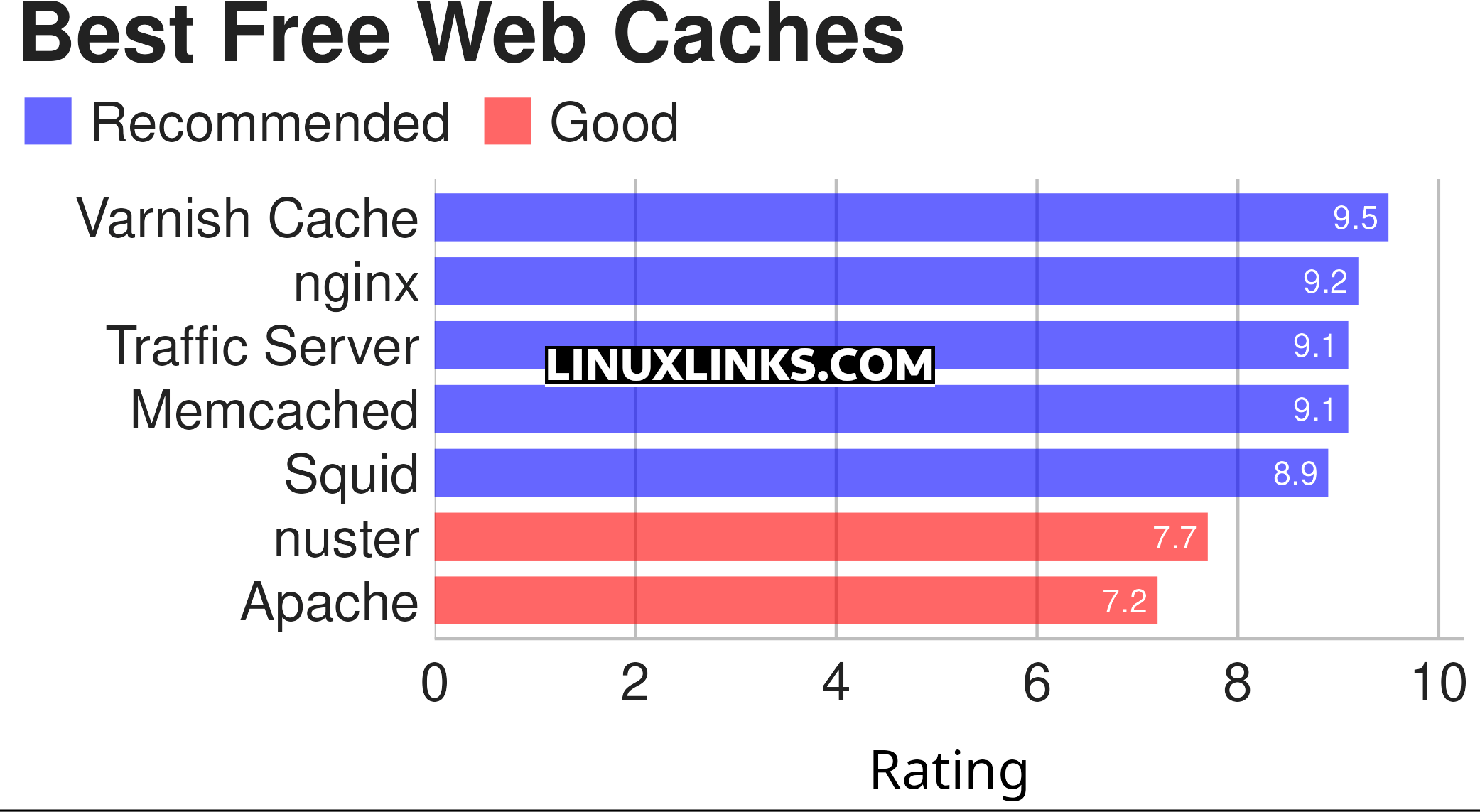
Let’s explore the 7 web caches. Click the links in the table below to learn about each application.
| Web Caches | |
|---|---|
| Varnish Cache | Web accelerator written with performance and flexibility in mind |
| nginx | Very powerful and efficient web server and reverse proxy |
| Traffic Server | High-performance building block for cloud services |
| Memcached | Distributed memory object caching system |
| Squid | High-performance proxy caching server and web cache daemon |
| nuster | High-performance HTTP proxy cache server |
| Apache | Hugely popular web server with caching modules |
This article has been revamped in line with our recent announcement.
 Read our complete collection of recommended free and open source software. Our curated compilation covers all categories of software. Read our complete collection of recommended free and open source software. Our curated compilation covers all categories of software. Spotted a useful open source Linux program not covered on our site? Please let us know by completing this form. The software collection forms part of our series of informative articles for Linux enthusiasts. There are hundreds of in-depth reviews, open source alternatives to proprietary software from large corporations like Google, Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, IBM, Cisco, Oracle, and Autodesk. There are also fun things to try, hardware, free programming books and tutorials, and much more. |
