A lightweight markup language is a modern system for annotating a document in a way that is syntactically distinguishable from the text.
Read more
The Linux Portal Site

A lightweight markup language is a modern system for annotating a document in a way that is syntactically distinguishable from the text.
Read more
There are some excellent alternative Python shells that extend on the basic shell. They each offer a good interactive Python experience.
Read more
CommonMark is a strongly defined, highly compatible specification of Markdown, along with a suite of comprehensive tests to validate implementations against the specification.
Read more
AsciiDoc is a lightweight markup language for writing notes, documentation, articles, books, ebooks, slideshows, web pages, man pages and blogs. It’s a plain text human readable/writable document format that dates back to 2002.
Read more
Textile converts its marked-up text input to valid, well-formed XHTML and also inserts character entity references for apostrophes, opening and closing single and double quotation marks, ellipses and em dashes. This lets users create documents, blogs and web pages without needing to write HTML.
Read more
Plain Old Documentation (known as pod) is a simple, lightweight markup language used for writing documentation for Perl, Perl programs, and Perl modules. This markup language is designed to make it easy for programmers to add documentation to their software and modules.
Read more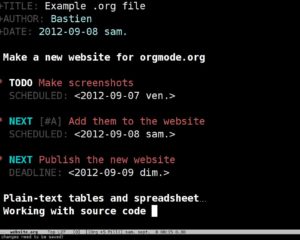
Natural language processing (NLP) is an exciting field of computer science, artificial intelligence, and computational linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human (natural) languages. It includes word and sentence tokenization, text classification and sentiment analysis, spelling correction, information extraction, parsing, meaning extraction, and question answering.
Read more
DocBook is a semantic markup language for writing structured documents using XML (or SGML). It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software but it can be used for any other sort of documentation. The language is fairly easy to learn; its strength derives from its flexibility.
Read more
reStructuredText (often abbreviated as reST) is an easy-to-read, what-you-see-is-what-you-get plaintext markup syntax and parser system. It’s designed to be a simple, unobtrusive markup language.
This lightweight markup language is useful for in-line program documentation (such as Python docstrings), technical documentation, for quickly creating simple web pages, as well as standalone documents.
Read more
Markdown is a plain text formatting syntax created by John Gruber in 2004. It’s designed to be easy-to-read and easy-to-write.
Readability is at the very heart of Markdown. It offers the advantages of plain text, provides a convenient format for writing for the web, but it’s not intended to be a replacement for HTML.
Read more