Last Updated on May 28, 2022
This is the eleventh in our series of articles highlighting essential system tools. These are small, indispensable utilities, useful for system administrators as well as regular users of Linux based systems. The series examines both graphical and text based open source utilities. For this article, we’ll look at Neofetch. For details of all tools in this series, please check the table at the bottom of the article.
Neofetch is a command-line interface system information script written in bash 3.2+. The script displays information about your system next to an image, your operating system logo, or any ASCII/image file of your choice. It’s designed to capture information about your system and display it in an aesthetic and visually pleasing way.
The main purpose of Neofetch is to convey to others the operating system or Linux distribution running on a system, together with critical information such as its hardware specifications, desktop environment, theme, icons, and a lot more besides.
Installation
Neofetch runs under all popular Linux distributions, and other operating systems. Popular distributions provide their own package, but installation is trivial in any event.
For example, in Ubuntu 17.04 and higher, type:
sudo apt update sudo apt install neofetch
In Operation
Neofetch’s configuration file is stored at ~/.config/neofetch/config. Provided the software is installed correctly, Neofetch copies its default configuration file to that location. You can edit that file so the script displays what you want.
Let’s first see an example of Neofetch’s output without using its config file.
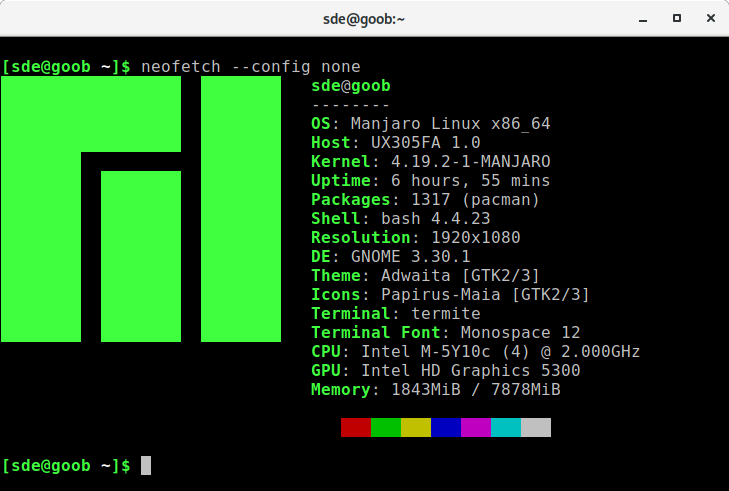
By default, the config file comments out some options including GPU Driver, disk information, battery information, and others. As I often use laptops, my config file enables battery and disk reporting. The image below reports that information in the final two lines.
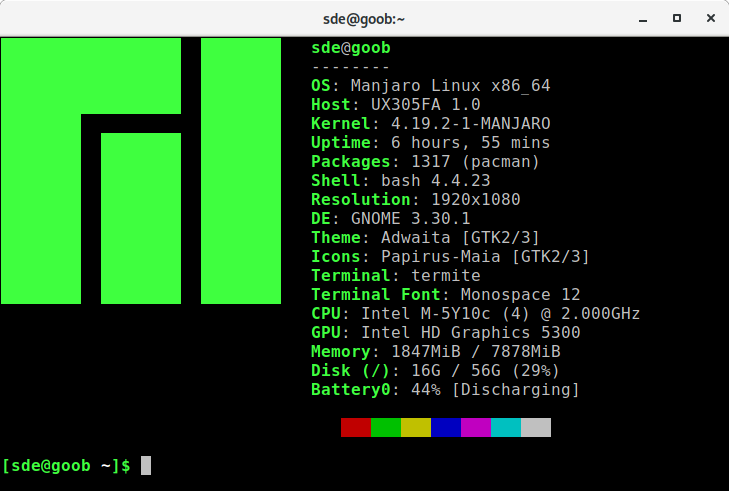
Neofetch is highly customizable through the use of command line flags or the user config file. The config file runs to a whopping 728 lines, and there’s tons of configuration options to tinker with, so that the output information may be tailored exactly to your requirements.
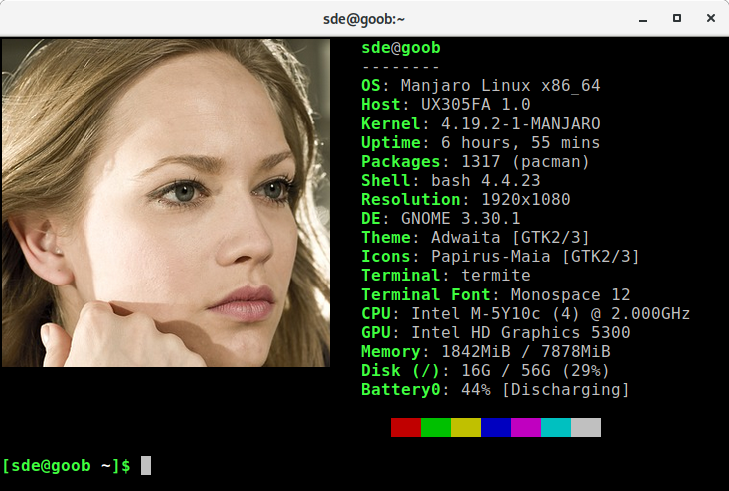
For example, you can change (or remove) the image displayed next to the system information. Here’s Neofetch displaying a PNG image file next to the system information. Note, not all terminal emulators can display images.
Summary
Neofetch offers an easy way to display information about a system. It’s extremely customizable and runs on any operating that supports Bash. Besides Linux, you’ll find it running on Mac OS X, iOS, Solaris, BSD, GNU Hurd, Android, Windows 10, and more.
As you can write your own Bash functions, the script can do just about anything you want.
Website: github.com/dylanaraps/neofetch
Support: Wiki
Developer: Dylan Araps
License: MIT License
Other tools in this series:
| Essential System Tools | |
|---|---|
| Alacritty | Innovative, hardware-accelerated terminal emulator |
| BleachBit | System cleaning software. Quick and easy way to service your computer |
| bottom | Graphical process/system monitor for the terminal |
| btop++ | Monitor usage and stats for CPU, memory, disks, network and processes |
| catfish | Versatile file searching software |
| Clonezilla | Partition and disk cloning software |
| CPU-X | System profiler with both a GUI and text-based |
| Czkawka | Find duplicate files, big files, empty files, similar images, and much more |
| ddrescue | Data recovery tool, retrieving data from failing drives as safely as possible |
| dust | More intuitive version of du written in Rust |
| f3 | Detect and fix counterfeit flash storage |
| Fail2ban | Ban hosts that cause multiple authentication errors |
| fdupes | Find or delete duplicate files |
| Firejail | Restrict the running environment of untrusted applications |
| Glances | Cross-platform system monitoring tool written in Python |
| GParted | Resize, copy, and move partitions without data |
| GreenWithEnvy | NVIDIA graphics card utility |
| gtop | System monitoring dashboard |
| gWakeOnLAN | Turn machines on through Wake On LAN |
| hyperfine | Command-line benchmarking tool |
| HyFetch | System information tool written in Python |
| inxi | Command-line system information tool that's a time-saver for everyone |
| journalctl | Query and display messages from the journal |
| kmon | Manage Linux kernel modules with this text-based tool |
| Krusader | Advanced, twin-panel (commander-style) file manager |
| Nmap | Network security tool that builds a "map" of the network |
| nmon | Systems administrator, tuner, and benchmark tool |
| nnn | Portable terminal file manager that's amazingly frugal |
| pet | Simple command-line snippet manager |
| Pingnoo | Graphical representation for traceroute and ping output |
| ps_mem | Accurate reporting of software's memory consumption |
| SMC | Multi-featured system monitor written in Python |
| Timeshift | Reliable system restore tool |
| QDirStat | Qt-based directory statistics |
| QJournalctl | Graphical User Interface for systemd’s journalctl |
| TLP | Must-have tool for anyone running Linux on a notebook |
| Unison | Console and graphical file synchronization software |
| VeraCrypt | Strong disk encryption software |
| Ventoy | Create bootable USB drive for ISO, WIM, IMG, VHD(x), EFI files |
| WTF | Personal information dashboard for your terminal |
