Last Updated on December 24, 2022
Text-based user interface
In addition to the utility’s attractive GTK interface, there’s also the option to run the software from a console.
The command
$ cpu-x -N
starts the program with its text-based user interface.
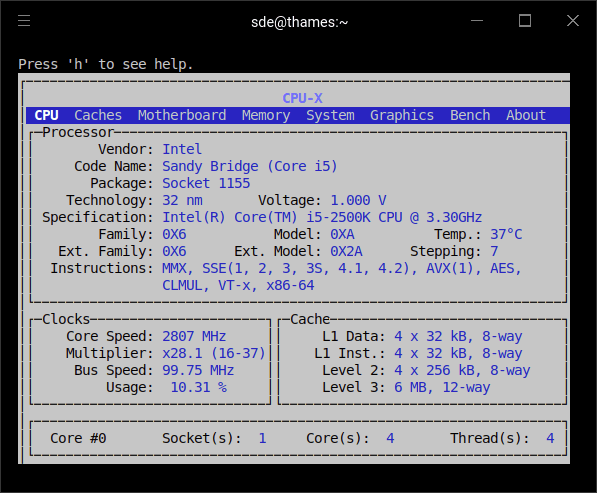
There’s support for Vim-keys and other key mappings.
There’s also the ability to dump all data to standard output and exit. This is performed by running the command:
$ cpu-x -D
This is a useful way to capture the system’s information and can be easily relayed to others; useful if you’re looking for help from others.
Pages in this article:
Page 1 – Introduction / Installation
Page 2 – In Operation
Page 3 – Text-based user interface
Page 4 – Summary
Complete list of articles in this series:
| Essential System Tools | |
|---|---|
| Alacritty | Innovative, hardware-accelerated terminal emulator |
| BleachBit | System cleaning software. Quick and easy way to service your computer |
| bottom | Process/system monitor for the terminal |
| btop++ | Monitor usage and stats for CPU, memory, disks, network and processes |
| catfish | Versatile file searching software |
| Clonezilla | Partition and disk cloning software |
| CPU-X | System profiler with both a GUI and text-based |
| Czkawka | Find duplicate files, big files, empty files, similar images, and much more |
| ddrescue | Data recovery tool, retrieving data from failing drives as safely as possible |
| dust | More intuitive version of du written in Rust |
| f3 | Detect and fix counterfeit flash storage |
| Fail2ban | Ban hosts that cause multiple authentication errors |
| fdupes | Find or delete duplicate files |
| Firejail | Restrict the running environment of untrusted applications |
| Glances | Cross-platform system monitoring tool written in Python |
| GParted | Resize, copy, and move partitions without data |
| GreenWithEnvy | NVIDIA graphics card utility |
| gtop | System monitoring dashboard |
| gWakeOnLAN | Turn machines on through Wake On LAN |
| hyperfine | Command-line benchmarking tool |
| HyFetch | System information tool written in Python |
| inxi | Command-line system information tool that's a time-saver for everyone |
| journalctl | Query and display messages from the journal |
| kmon | Manage Linux kernel modules with this text-based tool |
| Krusader | Advanced, twin-panel (commander-style) file manager |
| Nmap | Network security tool that builds a "map" of the network |
| nmon | Systems administrator, tuner, and benchmark tool |
| nnn | Portable terminal file manager that's amazingly frugal |
| pet | Simple command-line snippet manager |
| Pingnoo | Graphical representation for traceroute and ping output |
| ps_mem | Accurate reporting of software's memory consumption |
| SMC | Multi-featured system monitor written in Python |
| Timeshift | Reliable system restore tool |
| QDirStat | Qt-based directory statistics |
| QJournalctl | Graphical User Interface for systemd’s journalctl |
| TLP | Must-have tool for anyone running Linux on a notebook |
| Unison | Console and graphical file synchronization software |
| VeraCrypt | Strong disk encryption software |
| Ventoy | Create bootable USB drive for ISO, WIM, IMG, VHD(x), EFI files |
| WTF | Personal information dashboard for your terminal |

inxi is much better to be fair for sharing system information with others.
It’s what people usually recommend as far as I’ve seen. I’d have to check out how CPU-X differs before making any claims though.