Last Updated on May 22, 2022
7. Install BleachBit
With a fresh installation of Ubuntu you won’t have any junk festering on your system. But it doesn’t take long before a system needs cleaning. It’s best to get into good habits and periodically cleanse your system.
BleachBit deletes unnecessary files to free valuable disk space, maintain privacy, and remove junk. It removes cache, Internet history, temporary files, cookies, and broken shortcuts.
The program also wipes free disk space (to hide previously deleted files for privacy and to improve compression of images), vacuums Firefox databases (to improve performance without deleting data), and securely shreds arbitrary files.
We can install BleachBit from the Ubuntu Software program or from the command-line with the command:
$ sudo apt install bleachbit
Here’s BleachBit in action.
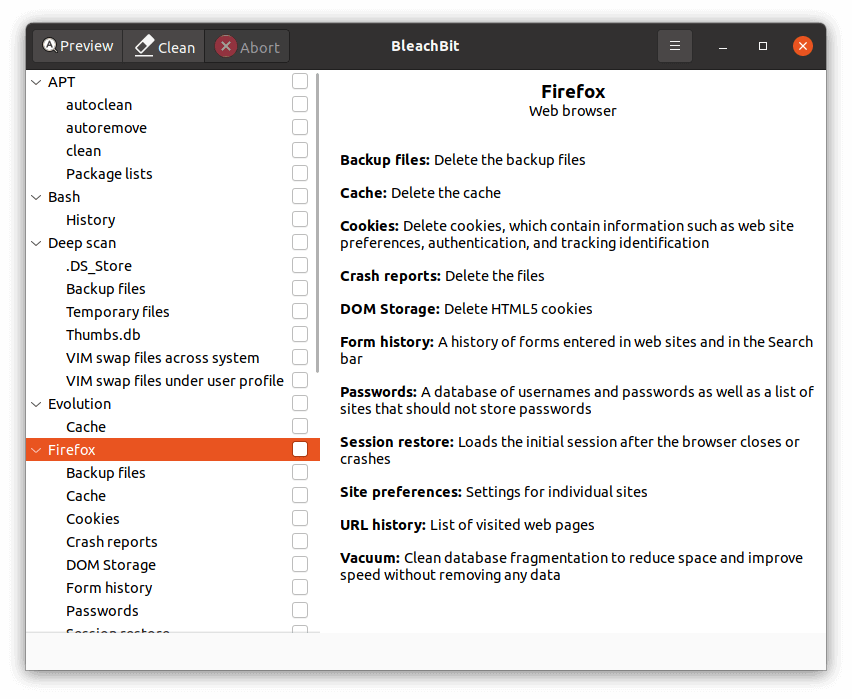
We’ve written a detailed review of BleachBit.
Next Page: Page 8 – Enable Night Light & Summary
Pages in this article:
Page 1 – Initial Update
Page 2 – Install Drivers
Page 3 – Enable Backups
Page 4 – Video/Audio Codecs and TrueType Fonts
Page 5 – GNOME Tweaks
Page 6 – GNOME Extensions
Page 7 – Install BleachBit
Page 8 – Night Light and Summary
All articles in this series:

Why only cover Ubuntu?
From independent surveys Ubuntu is the most popular Linux distro. Ignore the charts you see on some web sites that often have fairly obscure distros top. Their fanboys just vote them up using bots, partly because they are very passionate about them.
Interestingly, Linus Torvalds (the creator of the Linux kernel) has never even tried Ubuntu.
What about the command line? Newcomers shouldn’t only use GUIs in my opinion.
How about what to do when app doesnt have a package?
How about as a Linux user you whine, cry and criticize ever tutorial and article ever printed? It really gets old. I use Linux, I use Ubuntu, I use other OS’s. I appreciate people with the skill and knowledge to write tutorials and articles that can help others. No article can cover ‘everything Linux”. Thank you Steve.
We welcome suggestions what information you think is helpful for newcomers to Linux. When you’ve been using Linux for as long as we have, it’s easy to overlook things which would help beginners.
We will be covering the command-line in a later part of this series. But there’s a few important areas we need to cover first.