Storage Manager
This system utility offers a unified view of all your storage resources, including internal drives, external drives, and cloud storage services.
With Storage Manager, you manage your storage resources, allocate space as needed, and optimize your storage for better performance and reliability.
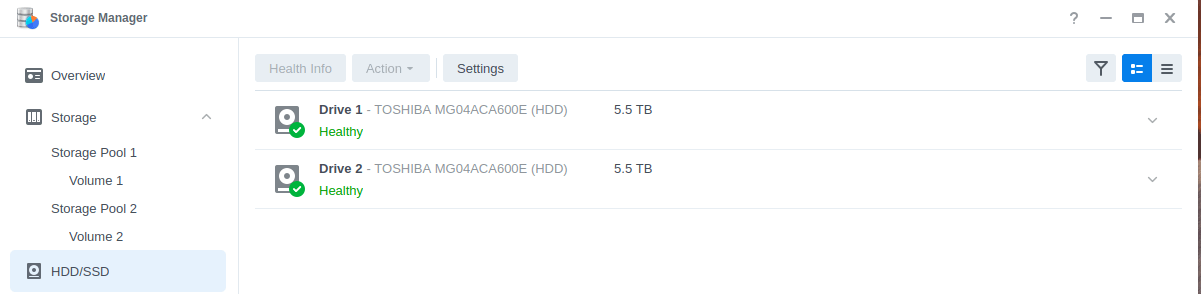
Storage Manager lets you create volumes and configure RAID settings. You need to create at least one volume and storage pool. The storage pool is essentially all hard drives grouped together, where a volume is where data is put on top.
I’ve actually set up my disks as JBOD, as this will be useful for my forthcoming open source Linux backup series. But most home users should use Synology Hybrid RAID (SHR) as it is proven, reliable, offers redundancy and flexibility. Remember the redundancy offered by SHR (or say RAID 5, RAID 6) simply gives data availability but you still need a separate backup strategy. I’ll look at backup solutions available directly from DSM in a couple of articles to be published.
Next page: Page 6 – Security Advisor
Pages in this article:
Page 1 – DSM Interface
Page 2 – File Station
Page 3 – Package Center
Page 4 – Control Panel
Page 5 – Storage Manager
Page 6 – Security Advisor
Page 7 – Summary
Page 8 – Appendix: Access the NAS using SMB on your local Linux machine
All articles in this series:
| Synology DSM | |
|---|---|
| DSM | Review of DiskStation Manager 7.2.1 |
| Container Manager | Container Manager for Beginners |
| Hyper Backup | This is a tutorial showing you how to use Hyper Backup |
| Hyper Backup Explorer | Desktop tool for browsing, decrypting, and extracting backup data |
